Notes
Cylinders and prisms
Calculating the volume of a cylinder or a prism is straightforward if we can easily calculate the area of the base.
- The volume of a cylinder or a prism is given by base area x height (perpendicular to the base).
- Example 1: Calculate the volume of a cylinder comprised of a circular base with a radius of 5 cm and a height of 6 cm. Volume = base area x height = (π x r2) x h = (π x 52) x 6 = 150π = 150(3.14) = 471 cm3.
- Example 2: Calculate the volume of a prism comprised of the following shape as the base and a height of 6 cm.
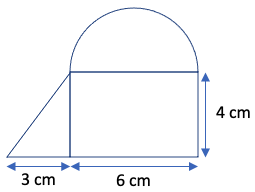
Half-circle area = (1/2) x π x r2 = (1/2) x π x (6/2)2 = 4.5π = 4.5(3.14) = 14.13 cm2.
Triangle area = (1/2) x b x h = (1/2) x 3 x 4 = 6 cm2.
Rectangle area = l x w = 6 x 4 = 24 cm2.
Base area = 14.13 cm2 + 6 cm2 + 24 cm2 = 44.13 cm2.
Volume = base area x height = 44.13 x 6 = 265 cm3.
Cones and pyramids
Calculating the volume of a cone or a pyramid is also straightforward if we can easily calculate the area of the base.
- The volume of a cone or a pyramid is given by (1/3) x base area x height (perpendicular to the base).
- Example 3: Calculate the volume of a cone comprised of a circular base with a radius of 5 cm and a height of 6 cm. Volume = (1/3) x base area x height = (1/3) x (π x r2) x h = (1/3) x (π x 52) x 6 = 50π = 50 x 3.14 = 157 cm3.
- Example 4: Calculate the volume of a pyramid comprised of a square base with side length 5 cm and a height of 6 cm. Volume = (1/3) x base area x height = (1/3) x (l x w) x h = (1/3) x (5 x 5) x 6 = 50 cm3.
Spheres
The formula for the volume of a sphere isn’t quite as well-known as the formula for the area of a circle, but it’s somewhat similar.
- The volume of a sphere is given by (4/3) x π x r3.
- Example 5: Calculate the volume of a sphere with a radius of 6 cm. Volume = (4/3) x π x r3 = (4/3) x π x 63 = 288π = 288 x 3.14 = 904 cm3.
Scaling
Length, area, and volume problems sometimes involve one or more measurements changing or scaling.
- Example 6: In 9.3: Area and perimeter, we calculated the circumference and area of a circle with a radius of 5 cm to be 31.4 cm and 78.5 cm2, respectively. Use these values to calculate the circumference and area of a circle with a radius of 10 cm. The scale factor here is 10/5 = 2.
- To calculate a new length (such as the circumference), we multiply by the scale factor. So, circumference of a 10 cm radius circle = 2 x circumference of a 5 cm radius circle = 2 x 31.4 cm = 62.8 cm.
- To calculate a new area, we multiply by the scale factor squared. So, area of a 10 cm radius circle = 22 x area of a 5 cm radius circle = 4 x 78.5 cm = 314 cm2.
- Example 7: In 9.4: Volume and scaling, we calculated the volume of a cylinder comprised of a circular base with a radius of 5 cm and a height of 6 cm to be 471 cm3.
- Use this value to calculate the volume of a cylinder comprised of a circular base with a radius of 10 cm and a height of 12 cm. The scale factor here is 10/5 = 12/6 = 2. To calculate the new volume, we multiply by the scale factor cubed. So, volume of a 10 cm radius 12 cm tall cylinder = 23 x volume of a 5 cm radius 6 cm tall cylinder = 8 x 471 = 3,768 cm3.
- What if just the radius doubles but not the height? Then the base area increases by a factor of 22 = 4 but the height stays the same. So, volume of a 10 cm radius 6 cm tall cylinder = 22 x volume of a 5 cm radius 6 cm tall cylinder = 4 x 471 = 1,884 cm3.
- What if just the height doubles but not the radius? Then the height increases by a factor of 2 but the base area stays the same. So, volume of a 5 cm radius 12 cm tall cylinder = 2 x volume of a 5 cm radius 6 cm tall cylinder = 2 x 471 = 942 cm3.
The video below works through some volume and scaling calculations.
Video Tips
Practice Exercises
Do the following exercises to practice volume and scaling calculations.

