Notes
When measuring the size of an object, we specify a number of measurement units. For example:
- Length is a one-dimensional (1D) measurement with units such as kilometres (km) or miles.
- Area is a two-dimensional (2D) measurement with units such as square metres (m2) or square feet (ft2).
- Volume is a three-dimensional (2D) measurement with units such as cubic centimetres (cm3) or cubic inches (in3).
Converting one measurement unit to another
Dimensional analysis is a flexible method for converting one measurement unit to another. Within the metric system, the calculations are straightforward. For example:
- Express 10 metres in centimetres. Since there are 100 centimetres in 1 metre, the fraction 100 cm / 1 m is equal to 1. We can multiply 10 m by 100 cm / 1 m so that the metre units cancel and we’re left with centimetre units:
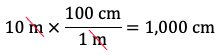
Therefore, 10 m is equal to 1,000 cm. - Express 10 metres in kilometres. Since there are 1,000 metres in 1 kilometre, the fraction 1 km / 1,000 m is equal to 1. We can multiply 10 m by 1 km / 1,000 m so that the metre units cancel and we’re left with kilometre units:
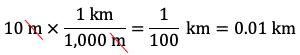
Therefore, 10 m is equal to 0.01 km.
Area conversions are similar, but we need to remember that areas are measured in square units. For example:
- Express 10 m2 in cm2. Since there are 100 cm in 1 m, there are 1002 cm2 in 12 m2, i.e., there are 10,000 cm2 in 1 m2. Therefore, the fraction 10,000 cm2 / 1 m2 is equal to 1:
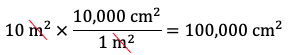
Therefore, 10 m2 is equal to 100,000 cm2 or 1 x 105 cm3. - Express 10 m2 in km2. Since there are 1,000 m in 1 km, there are 1,0002 m2 in 12 km2, i.e., there are 1,000,000 m2 in 1 km2. Therefore, the fraction 1 km2 / 1,000,000 m2 is equal to 1:
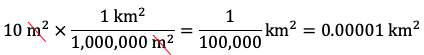
Therefore, 10 m2 is equal to 0.00001 km2 or 1 x 10–5 km3
Volume conversions are similar, but we need to remember that volumes are measured in cubic units. For example:
- Express 10 m3 in cm3. Since there are 100 cm in 1 m, there are 1003 cm3 in 13 m3, i.e., there are 1,000,000 cm3 in 1 m3. Therefore, the fraction 1,000,000 cm3 / 1 m3 is equal to 1:
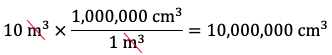
Therefore, 10 m3 is equal to 10,000,000 cm3 or 1 x 107 cm3. - Express 10 m3 in km3. Since there are 1,000 m in 1 km, there are 1,0003 m3 in 13 km3, i.e., there are 1,000,000,000 m3 in 1 km3. Therefore, the fraction 1 km3 / 1,000,000,000 m3 is equal to 1:
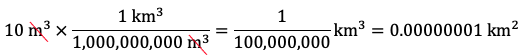
Therefore, 10 m3 is equal to 0.00000001 km3 or 1 x 10–8 km3.
Dimensional analysis can also handle trickier conversions between the metric system and the U.S. customary system. For example:
- Express 10 metres in inches. Since there are 100 cm in 1 m, the fraction 100 cm / 1 m is equal to 1. Also, since there are 2.54 cm in 1 inch, the fraction 1 inch / 2.54 cm is equal to 1. We can multiply 10 m by 100 cm / 1 m so that the metre units cancel and by 1 inch / 2.54 cm so that the cm units cancel and we’re left with inch units:
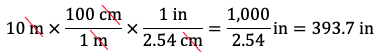
Therefore, 10 m is equal to 393.7 in. - Express 10 metres in feet. Extend the previous calculation by multiplying by 1 ft / 12 in:
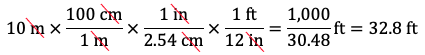
Therefore, 10 m is equal to 32.8 ft.
Dimensional analysis can also handle other types of conversions such as speed. For example:
- Express 10 metres per second in miles per hour. We need to convert metres in the numerator and seconds in the denominator to miles in the numerator and hours in the denominator.
- Multiplying by 1 km / 1,000 m will cancel the metres and leave kilometres in the numerator.
- Then multiplying by 1 mile / 1.6 km will cancel the kilometres and leave miles in the numerator.
- Multiplying by 60 secs / 1 min will cancel the seconds and leave minutes in the denominator.
- Then multiplying by 60 mins / 1 hour will cancel the minutes and leave hours in the denominator.
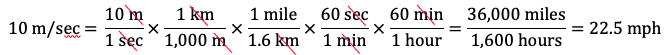
Therefore, 10 metres per second is approximately 22.5 miles per hour. (Using 1 mile = 1.61 km results in a more accurate answer of 22.4 mph.)
The video below works through some examples of using dimensional analysis to convert one measurement unit to another.
Video Tips
Practice Exercises
Do the following exercises to practice using dimensional analysis to convert one measurement unit to another.

